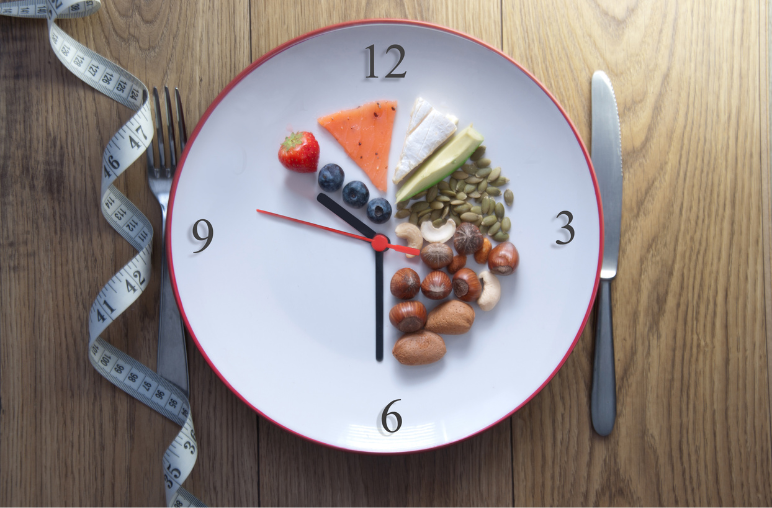
Autophagy fasting represents one of the most powerful tools for cellular health and longevity. This natural process occurs when your body shifts into survival mode during periods without food. Your cells begin breaking down damaged components and recycling them into newer, healthier structures. Research shows that autophagy fasting triggers profound changes at the cellular level, leading to improved health outcomes and potentially extended lifespan.
Understanding Autophagy: Your Body’s Cellular Cleanup System
Autophagy literally means “self-eating” in Greek. This process serves as your body’s internal recycling program. During autophagy fasting, cells identify damaged organelles, misfolded proteins, and cellular debris. They then package these components into specialized structures called autophagosomes.
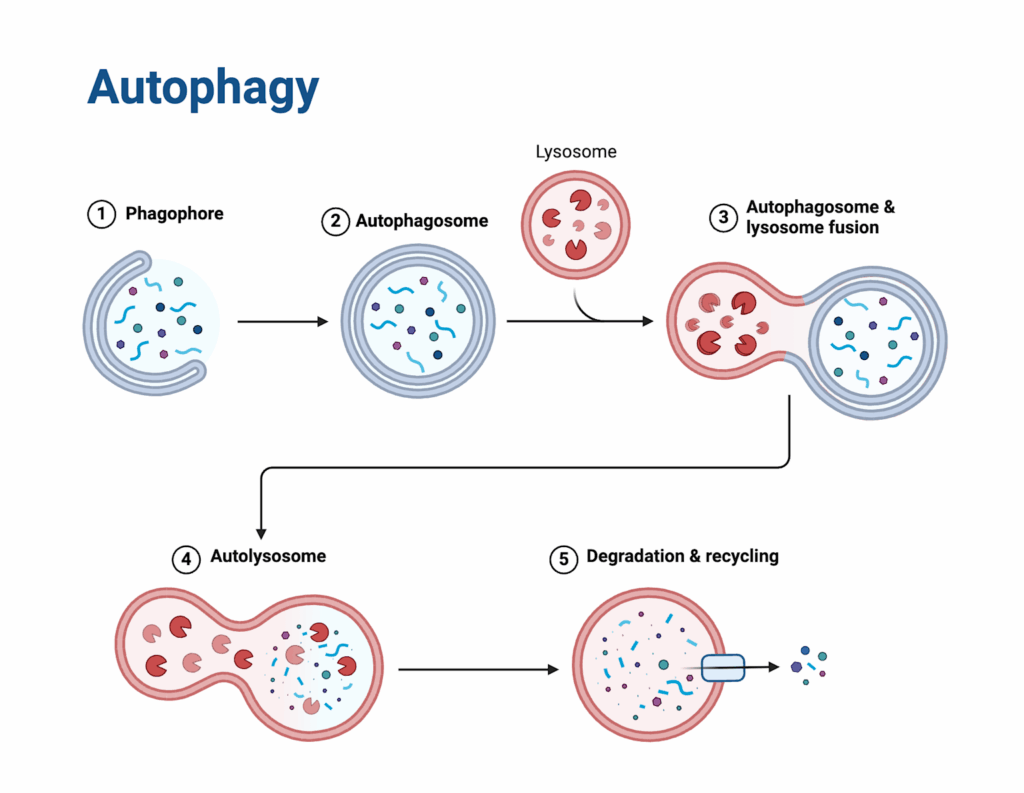
The autophagy process follows a precise sequence. First, cells form isolation membranes around damaged components. These membranes develop into autophagosomes that transport cellular waste to lysosomes. Lysosomes contain powerful enzymes that break down the waste materials. The resulting components get recycled back into the cell for energy and building blocks.
The Science Behind Cellular Renewal
Research demonstrates that autophagy fasting activates when nutrient levels drop significantly. Your body responds to energy stress by switching from growth mode to maintenance mode. This metabolic shift triggers the AMPK pathway while suppressing mTOR signaling. These changes signal cells to begin their cleanup operations.
Scientists have identified several types of autophagy. Macroautophagy handles large cellular components like organelles. Microautophagy involves direct engulfment of cellular material by lysosomes. Chaperone-mediated autophagy selectively targets specific proteins for degradation.
How Fasting Triggers Autophagy
Autophagy fasting works by creating controlled stress on your cells. When you stop eating, several metabolic changes occur that promote cellular cleanup.

Metabolic Switching During Fasting
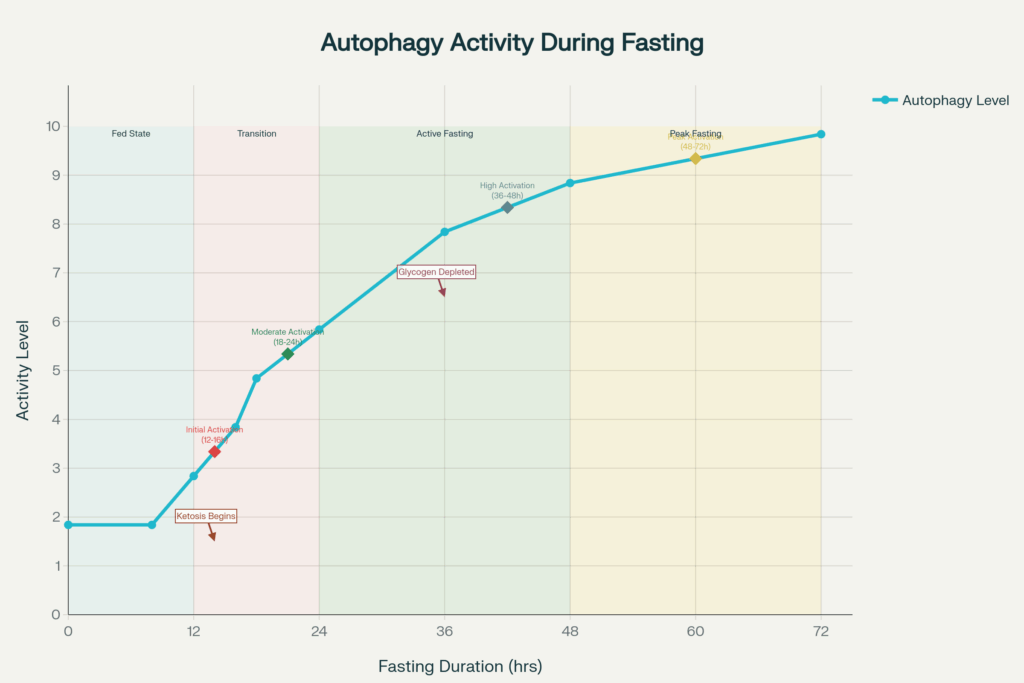
Your liver stores glucose as glycogen during fed states. After 12-16 hours of fasting, glycogen stores become depleted. Your body then shifts to burning stored fat for energy. This process produces ketones, which serve as alternative fuel sources for your brain and other organs.
The transition to ketosis marks a critical point in autophagy fasting. Ketone production signals your cells that energy is scarce. This triggers the activation of autophagy pathways throughout your body.
Hormonal Changes That Promote Autophagy
Autophagy fasting creates specific hormonal changes that enhance cellular cleanup. Insulin levels drop significantly during fasting periods. Lower insulin allows glucagon levels to rise, which promotes fat burning and autophagy activation.
Growth hormone levels increase during extended fasting periods. This hormone helps preserve muscle mass while promoting fat oxidation. The combination of low insulin and high growth hormone creates optimal conditions for autophagy fasting.
Timing Your Autophagy Fasting Protocol
Different fasting durations activate autophagy to varying degrees. Understanding these timeframes helps you optimize your autophagy fasting approach.
Short-Term Fasting (12-24 Hours)
Basic autophagy activation begins after 12-16 hours of fasting. This represents the minimum threshold for triggering cellular cleanup processes. Many people achieve this through overnight fasting combined with delayed breakfast.
The popular 16:8 method involves fasting for 16 hours daily. This approach provides consistent autophagy activation while remaining sustainable for most people.
Extended Fasting (24-48 Hours)
Autophagy activity increases significantly during 24-48 hour fasting periods. Research shows that longer fasts produce more robust cellular cleanup. However, extended fasting requires careful planning and medical supervision for some individuals.
Prolonged Fasting (48+ Hours)
Maximum autophagy activation occurs during fasts lasting 2-4 days. These extended periods produce the most dramatic cellular renewal benefits. Prolonged autophagy fasting should only be attempted under medical guidance.
Health Benefits of Autophagy Fasting
Scientific research reveals numerous health benefits associated with autophagy fasting. These benefits extend far beyond simple weight loss.
Longevity and Anti-Aging Effects
Studies show that autophagy fasting promotes longevity through multiple mechanisms. Cellular cleanup removes damaged proteins that contribute to aging. This process helps maintain cellular function and may extend lifespan.
Research on various organisms demonstrates that autophagy activation correlates with increased longevity. Animals with enhanced autophagy activity live longer and remain healthier throughout their extended lifespans.
Neuroprotection and Brain Health
Autophagy fasting provides significant benefits for brain health. The process removes protein aggregates associated with neurodegenerative diseases. This includes the toxic proteins found in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels increase during autophagy fasting. BDNF promotes neuron growth and protects existing brain cells. These effects contribute to improved cognitive function and memory.
Cardiovascular Benefits
Heart health improves through multiple autophagy fasting mechanisms. The process reduces inflammation markers linked to cardiovascular disease. Autophagy also helps remove damaged mitochondria from heart muscle cells, improving cardiac efficiency.
Blood pressure and cholesterol levels often improve with regular autophagy fasting. These changes reduce overall cardiovascular risk and promote long-term heart health.
Cancer Prevention and Treatment Support
Autophagy fasting shows promise in cancer prevention and treatment support. The process removes damaged cellular components that could become cancerous. This preventive effect may reduce cancer risk over time.
Research indicates that autophagy fasting may enhance chemotherapy effectiveness. Cancer cells often rely heavily on nutrients for rapid growth. Fasting creates metabolic stress that healthy cells tolerate better than cancer cells.
Popular Autophagy Fasting Methods
Several fasting approaches effectively trigger autophagy activation. Choose methods that fit your lifestyle and health status.
Time-Restricted Eating
The 16:8 method remains the most popular autophagy fasting approach. Fast for 16 hours daily and eat within an 8-hour window. This method provides consistent autophagy activation while remaining socially practical.
The 14:10 method offers a gentler introduction to autophagy fasting. Fast for 14 hours and eat within 10 hours. This approach works well for beginners or those with demanding schedules.
Alternate Day Fasting
This method alternates between fasting days and regular eating days. Complete fasting days provide intense autophagy activation. Modified versions allow 500-600 calories on fasting days.
Weekly Extended Fasts
The 5:2 method involves two fasting days per week with normal eating the other five days. This approach provides regular autophagy activation without daily restrictions.
Optimizing Your Autophagy Fasting Results
Several strategies can enhance the effectiveness of your autophagy fasting protocol.
Supporting Nutrients and Compounds
Certain compounds may boost autophagy activation during fasting:
- Coffee contains polyphenols that support cellular cleanup
- Green tea provides antioxidants that enhance autophagy
- Turmeric compounds may increase autophagy activity
- Spermidine from foods like aged cheese promotes cellular renewal
Exercise and Autophagy
Physical activity complements autophagy fasting perfectly. Exercise creates beneficial stress that triggers cellular cleanup in active tissues. High-intensity interval training may provide the strongest autophagy stimulus.
Combine exercise with fasting for maximum benefits. Working out during fasted states enhances both fat burning and autophagy activation.
Sleep and Recovery
Quality sleep supports autophagy processes throughout your body. Brain autophagy increases significantly during sleep, clearing metabolic waste from neural tissue. Prioritize 7-9 hours of quality sleep to maximize autophagy fasting benefits.
Safety Considerations and Precautions
Autophagy fasting provides significant benefits but requires careful consideration of safety factors.
Who Should Avoid Autophagy Fasting
Certain individuals should not attempt autophagy fasting without medical supervision:
- People with diabetes or blood sugar disorders
- Individuals taking medications that require food
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Those with eating disorder history
- People with certain chronic health conditions
Potential Side Effects
Some people experience side effects during initial autophagy fasting attempts:
These effects typically diminish as your body adapts to fasting protocols. Start gradually and increase fasting duration over time.
Medical Supervision
Consult healthcare providers before starting autophagy fasting, especially if you take medications or have health conditions. Some medications require adjustment during fasting periods. Blood pressure and diabetes medications may need modification.
Common Autophagy Fasting Mistakes
Avoid these common errors that reduce autophagy fasting effectiveness:
- Breaking fasts with processed foods instead of nutrient-dense options
- Overeating during feeding windows
- Inadequate hydration during fasting periods
- Ignoring hunger cues and pushing beyond safe limits
- Failing to adjust exercise intensity during longer fasts
Conclusion
Autophagy fasting represents a powerful tool for cellular health and longevity. This natural process helps your body remove damaged components while creating newer, healthier cellular structures. Research consistently demonstrates significant health benefits including improved brain function, cardiovascular health, and potential cancer prevention.
Start with shorter fasting periods like the 16:8 method and gradually increase duration as your body adapts. Support your autophagy fasting with quality nutrition, regular exercise, and adequate sleep. Always consult healthcare providers before beginning extended fasting protocols.
The science behind autophagy fasting continues evolving. Current research strongly supports its role in promoting health and longevity. By understanding how fasting triggers cellular cleanup, you can harness this natural process to optimize your health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How long do I need to fast to activate autophagy?
Autophagy begins activating after 12-16 hours of fasting, with significant activity occurring after 18-24 hours. Maximum activation typically requires 48-72 hours of fasting.
2. Is autophagy fasting safe for everyone?
No, people with diabetes, eating disorders, pregnant women, and those on certain medications should consult healthcare providers before attempting autophagy fasting.
3. Does drinking coffee break my autophagy fast?
Black coffee does not significantly interfere with autophagy and may actually enhance the process through beneficial polyphenols. Avoid adding milk, sugar, or other calories.
4. How often should I practice autophagy fasting?
The 16:8 method can be practiced daily, while longer fasts should be done less frequently. Start with 2-3 times per week and adjust based on your response.
5. Can I exercise during autophagy fasting?
Yes, moderate exercise complements autophagy fasting well. High-intensity exercise during longer fasts may cause excessive stress, so adjust intensity accordingly.
6. What should I eat when breaking an autophagy fast?
Break fasts with nutrient-dense whole foods including healthy fats, quality proteins, and vegetables. Avoid processed foods that can cause blood sugar spikes.
7. Will autophagy fasting help me lose weight?
Weight loss often occurs with autophagy fasting due to calorie restriction and improved metabolism. However, the primary benefits relate to cellular health rather than weight management.
8. How do I know if autophagy is working?
You may notice improved energy, better mental clarity, and enhanced sleep quality. However, autophagy occurs at the cellular level and cannot be directly measured without specialized testing.
Was this Blog Post useful to you?